Product List
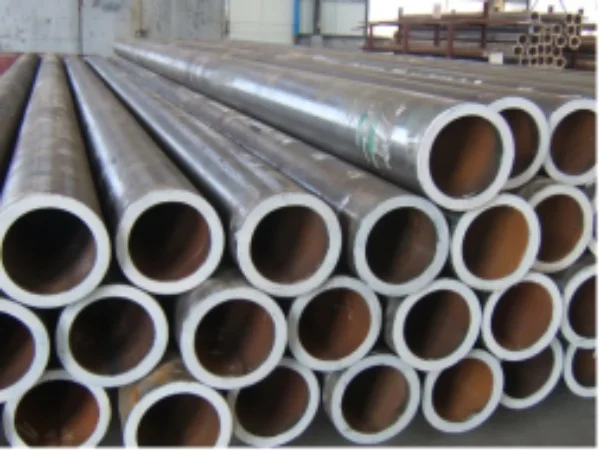
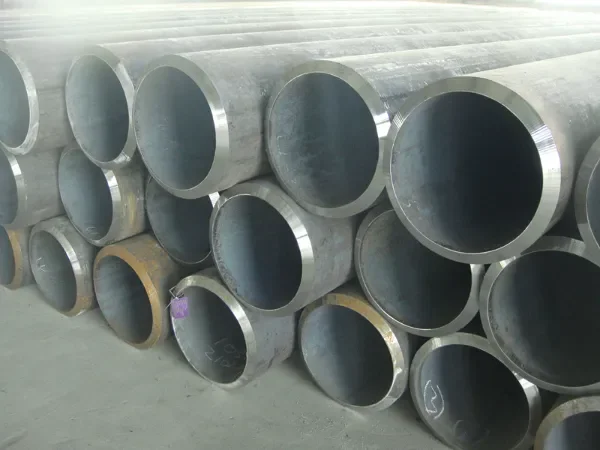
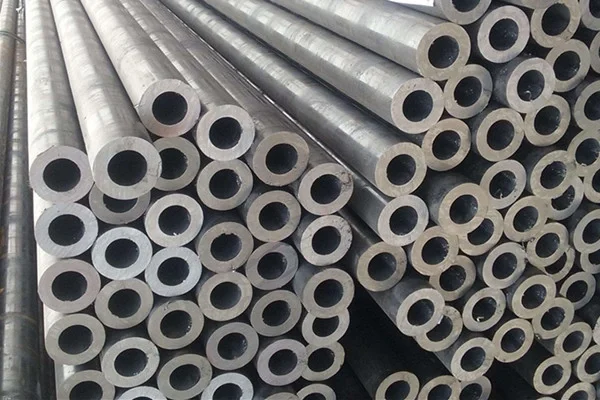
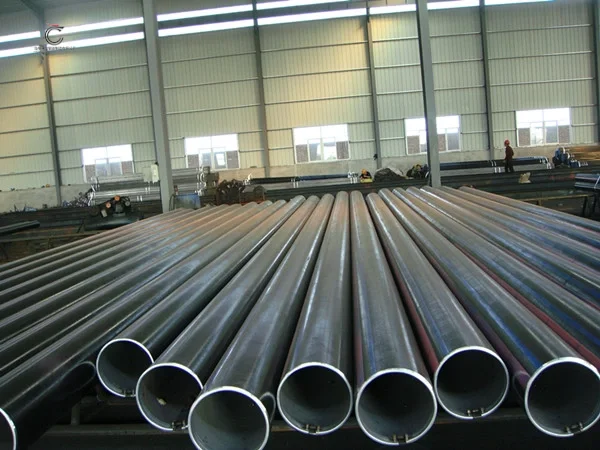
Boiler Pipe
Boiler steel pipes include medium-pressure boiler pipe and high-pressure boiler pipe, it is often manufactured in seamless procedures, and welded steel pipe is not applicable.
It has been widely used in heat exchanger pipe and tubing services, tube exchanger bundles, high-pressure boilers, economizers, superheaters, petrochemical industry pipes, etc.
Material and Standard of Boiler Pipe:
Standards and materials for steel pipe are available in carbon, alloy, and stainless steel material.
Carbon steel: ASTM/ASME A/SA 106, ASTM A179, ASTM A192, ASTM/ASME A/SA 210, ASTM A333 Gr 1, 6,7 to Gr 9,
Alloy steel: ASTM/ASME A/SA 213 T1, T2, T5, T9, T11, T12, T22, T91, T92; ASTM A335 P1, P2, P5, P9, P11, P12, P22, P91, P92
Stainless Steel: ASTM A268, ASTM A213, TP304/L, TP316/L, 310S,309S,317,317L,321,321H, and duplex stainless steel material etc.
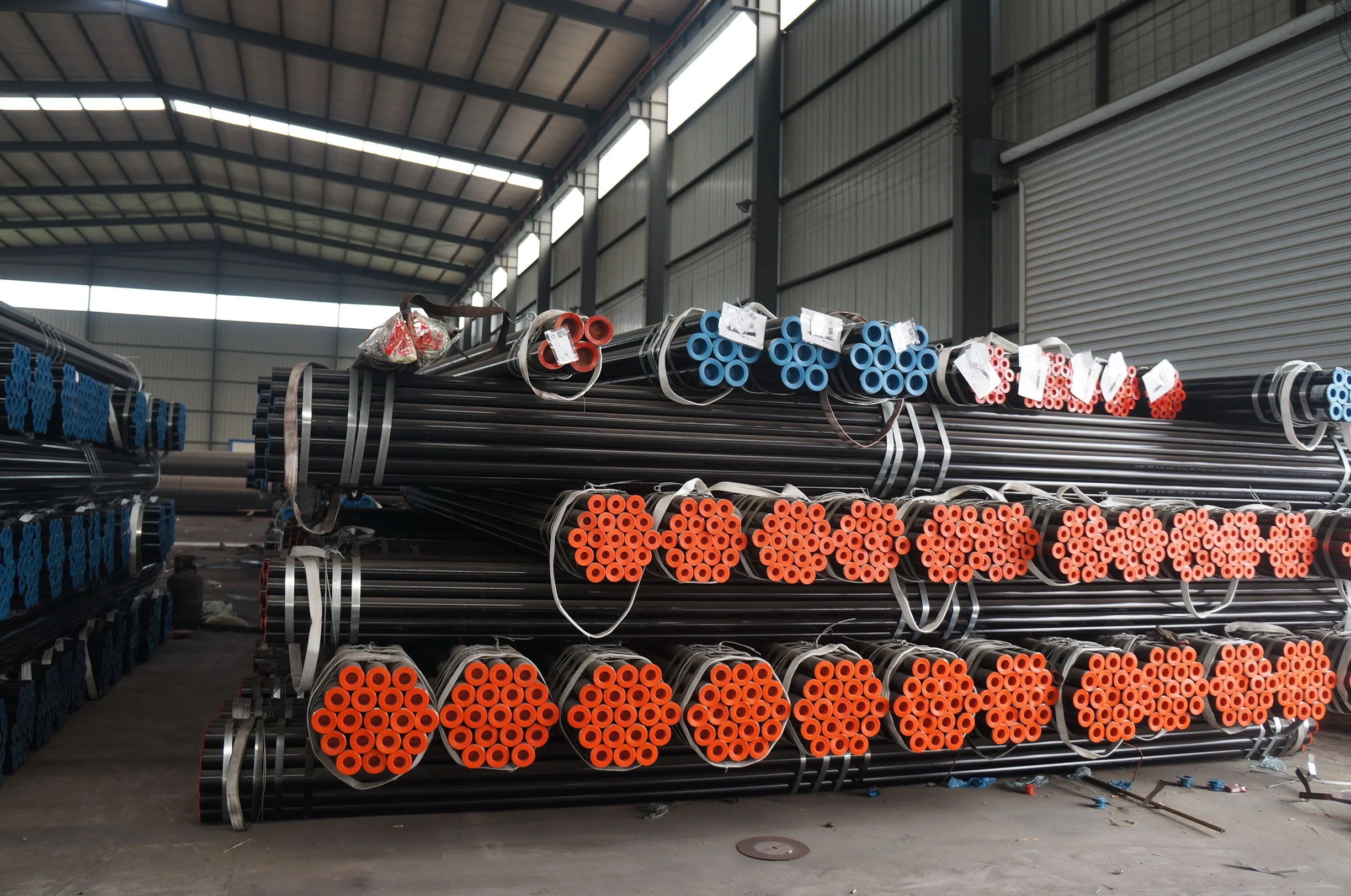
Common Sizes: OD from 6mm to 1240mm, thickness from 1mm to 50mm
Types: Straight boiler pipe, and U boiler steel pipe for tube exchanger bundle.
These standards specify the classification, size, shape, weight and allowable deviation, technical requirements, inspection and test, packaging, marking, and quality certificate of seamless steel tubes for the boiler.
Available Size Scope:
The boiler pipe size range complied with the different ASTM standards required. Like ASTM A106 or ASTM 179, 192, etc.
But most of the boiler pipe size is small, with outer diameter usually less than 1 1/2” (1/4”, 1/2”, 3/4”, 1” and 1 1/2”). Then 2”, 2 1/2”, 3” and maximum to 4”.
How to produce boiler pipes?
The manufacturing method of medium and high-pressure boiler steel pipe is the same as the seamless steel pipe, but there are some key manufacturing processes that shall be noted: Fine drawing, surface bright, hot rolling, cold drawing, and heat expansion
Heat treatment was applied to the boiler pipes
Heat treatment is one way of changing the physical properties of high-pressure boiler pipes by heating and cooling. Heat treatment can improve the microstructure of high-pressure boiler pipes, so as to meet the required physical requirements. Toughness, hardness, and wear resistance are obtained by heat treatment. In order to obtain these characteristics, it is necessary to adopt quenching, annealing, tempering, and surface hardening.
1). Quenching
Hardening, also called quenching, is when a high-pressure boiler pipe is heated evenly to the appropriate temperature, then quickly immerse in water or oil for rapid cooling, and cooling in the air or in the freezing zone. So that the high-pressure boiler pipe can obtain the required hardness.
2) Tempering
High-pressure boiler pipe will become brittle after hardening. And the stress caused by quenching can make the high-pressure boiler pipe tap and break. The tempering method can be used to eliminate brittleness. Although the hardness of high-pressure boiler pipe is lighter reduced, its toughness can be increased to reduce the brittleness.
3) Annealing
Annealing is the method to eliminate the internal stress of high-pressure boiler pipes. The annealing method is that the steel parts need to be heated to a critical temperature, then put in dry ash, lime, and asbestos or closed in the furnace, then let cool slowly.
Differences between medium and high-pressure boiler pipes:
On the basis of different working temperatures, the medium or high-pressure boiler pipe shall be used. Generally can be classified as below:
a.The operation temperature of the general boiler pipe is lower than 450℃. The medium-pressure boiler pipeline mainly adopts a hot rolling process or cold drawing process.
b. High-pressure boiler pipes are often used in high-temperature and high-pressure conditions. Under the action of high-temperature flue gas and steam, the pipe will occur oxidation and corrosion. It is required a high-pressure boiler pipe that has high durable strength, high oxidation corrosion resistance, and good tissue stability.