Product List
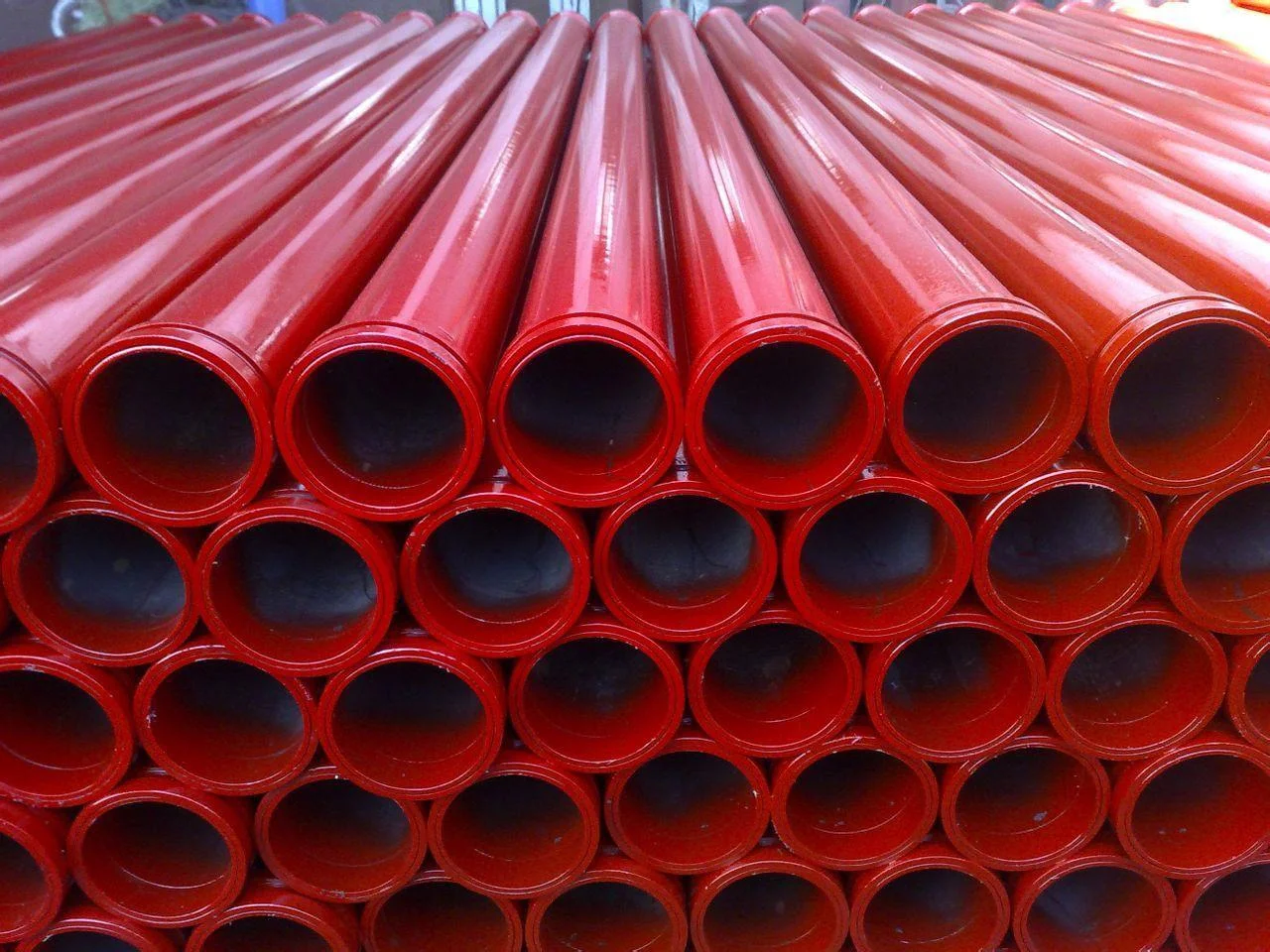
Hot Dip Galvanized Steel Pipe
Product name: Hot dip galvanized steel pipe, Hot dip galvanized hollow steel pipes, Hot dip galvanized pipe, welding galvanized fence pipe, hollow steel pipe, HDG steel pipe, galvanized pipe, Galvanized Steel Pipe,HDG steel tube
Standard: A53, EN10255, DIN2440, BS1387 etc.
Materials: Gr.B, S195T, ST35 etc.
Pipe galvanizing is the process of coating iron or steel with a layer of zinc. This helps to prevent corrosion and rust and is often used on pipes that will be exposed to the elements. The zinc provides a barrier against moisture and oxygen, which can cause iron and steel to corrode. In addition, zinc protects the metal from being damaged by ultraviolet light. The process of pipe galvanizing can be done in two ways: hot-dip galvanizing or pre-galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing involves dipping the pipes into a vat of molten zinc, while pre-galvanizing involves rolling galvanized coils into pipes. Both methods are effective at protecting the metal from corrosion, but hot-dip galvanizing is generally considered to be more durable. Pipe galvanizing is an important process that helps to prevent corrosion and rusting, and extends the life of metal pipes.
Hot dip galvanized steel pipe type
Hot dip galvanized hollow steel pipes, HDG hollow steel pipe, HDG square tube, HDG round tube, HDG rectangular tube, HDG erw welded pipe, HDG seamless pipe, HDG spiral welded pipe
Hot dip galvanized steel pipe specification
1. Standard: GB/T3091 - 2001, A53, EN10255, DIN2440, BS1387 etc.
2. Materials: Q235, Q345B, Gr.B, S195T, ST35 etc.
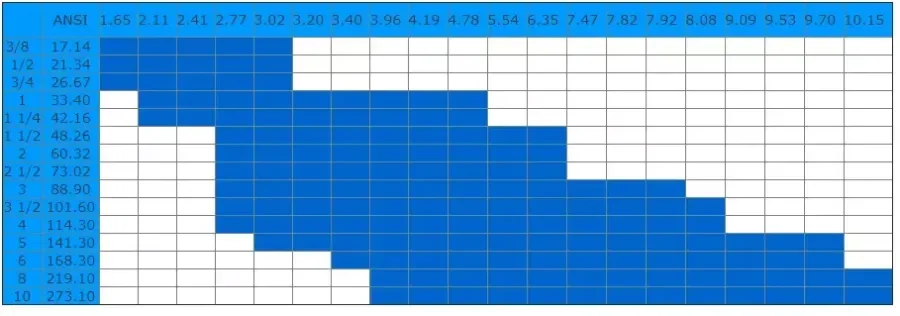
3. Outer diameter: 1/4" - 40"
Wall thickness: Sch5 - Sch80(1.0mm – 25.4mm).
Length: 2m - 12m.
4. Application: construction, fire control, pipeline etc.
Hot dip galvanized steel pipe advantages
Shenlong Hot dip galvanized steel pipe with a zinc layer thickness in accordance with ISO standards and good corrosion resistance.
WHY USING PIPE GALVANIZING?
Without pipe galvanizing, corrosion is a persistent danger to metal; therefore, it must be protected. It is possible to create oxidation in metal when corrosive elements such as salt, dirt, moisture, or chemicals come into contact with the iron in the metal. Rust is formed as a consequence of the reaction. Because of the corrosion of metal, pipes are at risk of collapsing or exploding.
Adding a coating of zinc to metal during the pipe galvanizing process serves to protect it against corrosion. This zinc reinforcement provides two types of protection for metals:
It acts as a protective barrier between the sensitive iron and the corrosive elements.
Galvanic corrosion is prevented by using this product. When compared to the majority of metals, zinc exhibits significantly anodic characteristics. When it comes into touch with a more noble metal, it acts as an anode, releasing electrons very immediately. When a noble metal would otherwise be taking electrons from carbon steel or another basic metal, this sacrifice comes in useful.
ADVANTAGES OF PIPE GALVANIZING
The hot dip galvanized steel pipe is to make the molten metal and iron substrate reaction, the alloy layer, so that the substrate and coating combination of both. Hot-dip galvanizing is the first steel pickling, in order to remove the steel pipe surface of iron oxide, pickling, aqueous solution of ammonium chloride or zinc chloride or ammonium chloride and zinc chloride mixed aqueous solution tank cleaning, and then send into the hot dip tank. Hot dip galvanized coating uniformity, strong adhesion, and long life.
Hot Dip Galvanized Steel Pipe Technical Data

What is hot dip galvanized steel pipe?
Hot dip galvanized steel pipe, in order to improve the corrosion resistance of the steel pipe, the general steel pipe is galvanized. Galvanized steel pipe is divided into two types: hot-dip galvanized and electro-galvanized. The hot-dip galvanized galvanized layer is thick, the cost of electro-galvanized is low, and the surface is not very smooth.
The hot dip galvanized steel pipe is to make the molten metal react with the iron matrix to produce an alloy layer, so that the matrix and the coating are combined. Hot-dip galvanizing is to pickle the steel pipe first. In order to remove the iron oxide on the surface of the steel pipe, after pickling, it is cleaned in the tank of ammonium chloride or zinc chloride aqueous solution or mixed aqueous solution of ammonium chloride and zinc chloride, and then sent to the in the hot dip bath. Hot-dip galvanizing has the advantages of uniform coating, strong adhesion and long service life. The steel tube substrate undergoes complex physical and chemical reactions with the molten plating solution to form a corrosion-resistant zinc-iron alloy layer with a compact structure. The alloy layer is integrated with the pure zinc layer and the steel tube substrate. Therefore, it has strong corrosion resistance.